Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing technology is currently one of the most popular and widely used 3D printing methods on the market. Thanks to its simple working principle, affordable cost, and ability to produce high-precision products, FDM has become an ideal choice for both individual users and businesses. Today, a wide range of FDM 3D printers have been developed with remarkable improvements in performance, durability, and flexibility, meeting diverse production needs from engineering prototypes to finished products.
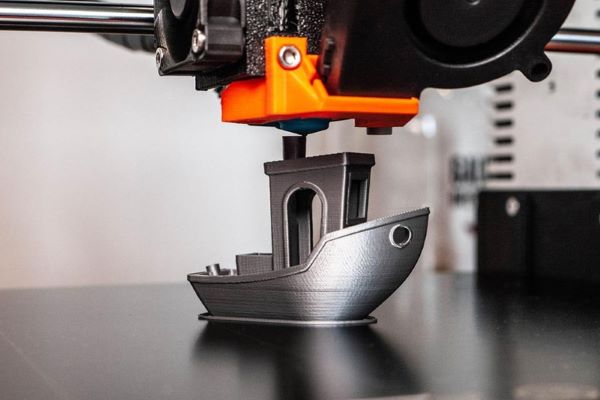

What is FDM 3D Printing?
FDM 3D printing (Fused Deposition Modeling) is a technology based on “fused filament fabrication,” developed in the late 1980s by S. Scott Crump. This method works by heating and melting thermoplastic filament, which is then extruded layer by layer to build a complete 3D model. With advantages such as low investment cost, simple operation, and a wide range of printable materials, FDM printers have become an ideal choice for applications in prototyping, education, and even consumer product manufacturing.

What is the working principle of an FDM printer?
The working principle of an FDM 3D printer is based on the technique of extruding melted thermoplastic to form stacked layers according to the design shape. The specific operating mechanism is as follows:

- First, the filament (most commonly PLA or ABS) is fed into the printer’s extruder.
- As the printer operates, the extruder heats the filament to its melting point, then pushes the molten plastic through a nozzle to form 2D print lines on the surface.
- Once a layer is completed, the extruder or the print bed moves to begin printing the next layer. This process is controlled by slicing software, which converts the model into G-code. The G-code guides the printer with precise instructions for movement, speed, and optimal temperature for each layer.
- For parts with overhangs or complex geometries, the printer uses support material. These supports can be easily removed after printing, ensuring the final product has both high accuracy and a refined finish.
- Thanks to its efficient and flexible operation, an FDM 3D printer can produce everything from small parts to complex technical models with excellent precision and aesthetic quality.
Common materials used in FDM printers
FDM 3D printing technology supports a wide range of thermoplastic materials, each with its own unique properties tailored to specific purposes and applications in manufacturing. Below are the most commonly used materials in FDM 3D printing:

- PLA (Polylactic Acid): This is the most commonly used filament in FDM printing due to its ease of use, eco-friendliness, and affordable cost. PLA is rigid, prints well at low temperatures, and is suitable for display models or products that don’t require high strength. However, it is relatively brittle and not durable under high temperatures or load-bearing environments.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Known for its mechanical strength, impact resistance, and higher heat tolerance compared to PLA. ABS is commonly used for engineering parts that require durability. However, it requires high printing temperatures, tends to emit unpleasant odors during printing, and needs a stable printing environment to avoid warping or shrinkage.
- PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified): PETG combines the ease of printing of PLA with the strength of ABS. It is tough, impact-resistant, less prone to cracking, and capable of producing transparent parts. PETG doesn’t require an enclosed printer and is ideal for applications needing moderate mechanical strength, clarity, or impact resistance.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is a flexible filament with high elasticity, excellent abrasion resistance, and good resistance to oil and chemicals. It is commonly used to print stretchable products such as phone cases, medical devices, or sports accessories. However, TPU requires advanced printing skills, as its flexible nature can cause clogs or sticking in the nozzle.
- PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone): A high-performance engineering material with exceptional heat resistance, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength. PEEK is widely used in demanding industries such as medical, aerospace, and precision engineering. However, it is expensive and requires specialized printers capable of extremely high temperatures for optimal performance.
Popular FDM 3D printer models today
Below are some notable FDM 3D printer models that are highly rated for their performance, design, and practical applications. Each model features unique strengths, making them suitable for a wide range of users from individual hobbyists to professional businesses.
Reprap Prusa I3
Among the various FDM 3D printer models available on the market, the Reprap Prusa i3 stands out as a prominent choice, especially favored by small businesses and tech enthusiasts. Compared to its predecessors, the Prusa i3 has been significantly improved in terms of print performance and stability, while the assembly process has become much more straightforward.
Users can choose to purchase a DIY kit and assemble it at home using detailed instructions provided. Alternatively, for those looking to save time, fully assembled machines are also available offering high build quality and stable operation.
Creatbot DE plus
The Creatbot DE Plus is a high-end FDM 3D printer designed with a range of advanced features for professional users. Some of its notable highlights include:
- Equipped with a nozzle featuring a blue heat sink, which enhances cooling efficiency and supports a wide range of printing materials.
- Offers customizable configurations for single, dual, or triple extruder heads depending on user needs.
- Delivers high precision up to 0.05 mm and fast print speeds of up to 200 mm/s.
- Built with a robust steel frame to ensure durability and printing stability.
- Large build volume of up to 400 x 300 x 520 mm.
- Fully enclosed print chamber to minimize external environmental interference.
- Power recovery feature allows the printer to resume printing from the exact point it stopped in case of a power outage.
- Modern touchscreen interface for easy and user-friendly operation.
Flashforge Creator 3
Flashforge Creator 3 is an FDM 3D printer known for its stable performance in a compact design, making it suitable for various working environments. Key features of the machine include:
- Dual extruder support, allowing simultaneous printing with two materials or two colors in a single print job.
- Build volume of 22.5 x 14.5 x 14.5 cm, suitable for many medium-sized design models.
- Compatible with a wide range of common materials such as ABS, PLA (1.75mm filament), colored nylon blends, and more.
- Reliable and easy to use, making it ideal for both beginners and professional users.
Cubicon style plus & style NEO
The Cubicon Style Plus and Style NEO models stand out with their modern design, quiet operation, and a range of advanced supporting technologies. Key features include:
- A sleek aluminum frame that ensures both durability and high aesthetic value.
- Fully enclosed printing mechanism that minimizes noise and vibration during operation.
- Certified 3-stage air filtration system that eliminates dust and odors generated during printing.
- Automatic filament loading module with built-in recognition and quality control for filament rolls.
- Stainless steel nozzle that is easy to replace, ensuring optimal print quality.
- Anti-slip ceramic-coated print bed with automatic heating capability.
- Auto-leveling system for both the print bed and print head, enhancing accuracy and optimizing the printing process.
From these outstanding features, it is clear that FDM 3D printing technology continues to evolve to meet increasing demands in design, manufacturing, and research. With its precision, cost-efficiency, and flexible applications, FDM remains a vital component in the modern manufacturing revolution. Choosing the right FDM printer model will help maximize work efficiency and unlock greater creative potential for users.