The structure of CNC machining machines is one of the key factors that makes mechanical processing easier and enables the creation of high-precision products. In addition to structure, understanding the classification and working principles of CNC machines also plays a crucial role in choosing and operating the machine effectively. To learn more about CNC machines, let’s explore the details with 3Dmanufacturer through the article below!
What is a CNC Machining Machine?
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining machine is an automated device used in mechanical processing, controlled by a computer to guide the movements of cutting tools, drills, or other instruments to produce complex and precise parts.
CNC technology began development in the late 1940s in the U.S., initially used mainly in metalworking for defense purposes. Over the years, CNC machines have become indispensable in many modern manufacturing sectors such as precision engineering, industrial woodworking, electronics, and healthcare.
Thanks to pre-programmed code (usually G-code), CNC machines offer fast processing speeds and high precision for cutting, drilling, and milling – up to 99% accuracy compared to design drawings.

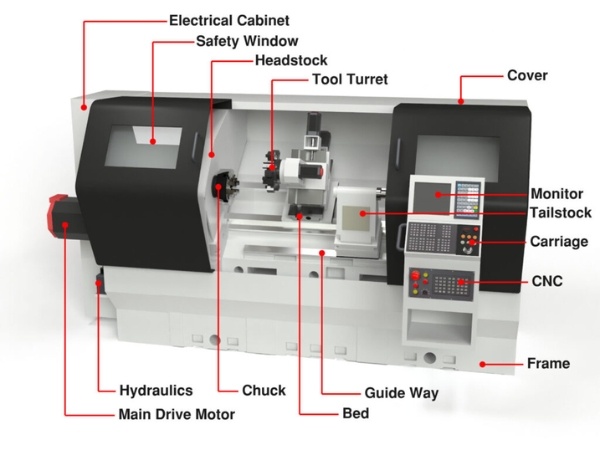
Structure of CNC Machining Machines
The structure of CNC machining machines is designed to operate efficiently in both 2D and 3D environments using professional design software. The key components and their functions in a typical CNC machine include:
Actuator system
The actuator system is the part that directly performs machining processes on the CNC machine, including key components such as:
Motors
In a CNC machine’s drive system, four types of motors are commonly used, each suitable for different technical requirements:
- DC motor (Direct Current): Uses permanent magnets for excitation. With low power consumption and minimal heat generation, DC motors provide high efficiency and reliability.
- AC motor (Alternating Current): High load capacity, high torque-to-inertia ratio, and stable operation even at low speeds. These are often found in high-performance CNC systems.
- Stepper motor: Converts electrical pulses into precise angular or linear movements. Common in smaller CNC machines or applications requiring step-by-step accuracy.
- Servo motor: Equipped with a feedback loop to adjust position and speed based on feedback signals. Preferred in closed-loop CNC systems for precise control and fast response.
Machine frame and base
The frame and base of the CNC machine bear the entire machine structure and absorb vibrations. Typically made from gray or alloy cast iron for high durability and rigidity.
The machine surface is precisely machined to install slideways, including two prism-shaped and two flat guideways, to ensure accurate movement of the tool carriage and tailstock.

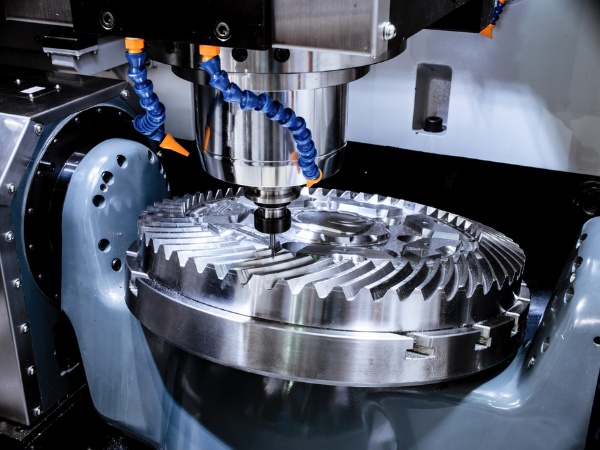
Work table
In the structure of CNC machining machine, the worktable is the component used to place and secure the workpiece, often combined with a fixture for precise positioning. The table can move along different axes (X, Y) depending on the design of each type of CNC machine.
Spindle
The spindle is a critical component that holds cutting tools like milling cutters, turning tools, and drills. It performs the main rotational movement in machining and works in tandem with linear movements along X, Y, and Z axes.
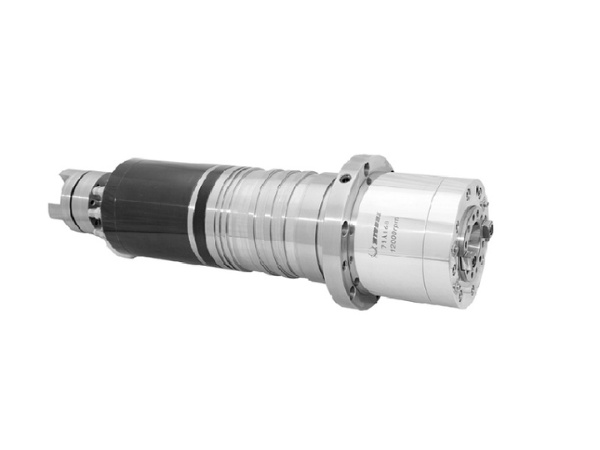

Spindle drive types include:
- Belt drive: The motor transmits power to the spindle via a belt.
- Direct drive: The motor connects directly to the spindle without belts or gears.
- Gearbox drive: Uses a gear system to provide high torque at low speeds – suitable for hard materials or large parts.
- Integrated spindle motor: The motor is built into the spindle itself – enabling high speed, accuracy, reduced vibration, and minimal power loss.
Guideways
Also known as linear guides or rails, these components guide the linear motion of the worktable or spindle assembly along the X, Y, and Z axes. They allow for smooth, accurate movement through rolling or sliding contact between the slider and rail.
In advanced CNC machines, the table may be stationary while the spindle and cutting head move freely in all directions to perform machining.
Lead screws and nuts
Lead screws and nuts convert rotary motion from the motor into linear motion of the worktable or slides. Two common types:
- Conventional lead screw: Involves surface contact, causing higher friction and backlash – less efficient and unsuitable for high-precision machines.
- Ball screw: Uses steel balls between the screw and nut to reduce friction via rolling contact, yielding minimal backlash and high transmission efficiency. Accuracy can reach 1/1000 inch per foot (~0.083 mm/meter).
Tool magazine
In the structure of CNC machining machine, the tool magazine is the component used to store various cutting tools required for the machining process. Each tool is placed in a separate, numbered slot within the magazine, allowing the machine to identify and select the correct tool.
When a tool change is needed during operation, the machine works in conjunction with an Automatic Tool Changer (ATC) to retrieve the correct tool from the magazine and install it into the spindle. This enables continuous machining without manual intervention by a technician, increasing production speed and minimizing the risk of human error.
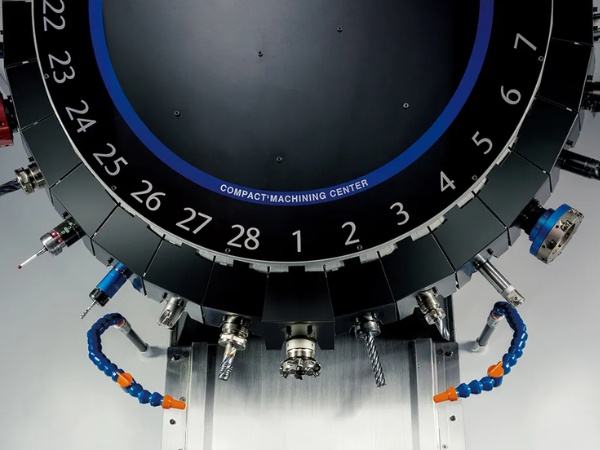

Control unit
The control unit includes the main control assembly and the various motors in the CNC machine.
Machine control unit (MCU)
The MCU is the brain of the CNC machine. It processes the CNC program (G-code), coordinates all machine operations, and often comes with a keypad or touchscreen for manual data input (MDI) or program loading from external memory.
When the CNC program is executed, the MCU decodes the instructions, identifies coordinates, speed, rotation direction, etc., and sends signals to drive motors → rotate the ball screw → move the table or cutter along the X, Y, Z axes.
MCU functions include:
- Decode and analyze G-code instructions.
- Send control signals to spindle, table, and motors.
- Handle interpolation commands (linear, circular, helical).
- Control axis movements via servo or stepper motor drivers.
- Monitor and adjust position/speed in real time using feedback signals.
Drive Assembly
In the structure of CNC machining machines, the drive assembly consists of components responsible for executing the mechanical movements of the CNC machine, including:
- Drive motors: Typically servo or stepper motors, controlling X, Y, Z axes.
- Feedback sensors: Such as encoders or resolvers, providing real-time signals to ensure accuracy.
- Amplifiers and servo controllers: Boost signals from the MCU to drive motors.
- Mechanical transmission: Includes ball screws, slides, and rails that transmit motion to the tool or worktable.
Working principle
CNC machines operate based on numerical control programs, mainly written in G-code. The workflow starts with designing and programming the part using CAD/CAM software, which is then uploaded into the MCU (Machine Control Unit).
The MCU interprets the commands and sends signals to drive systems like servo or stepper motors. These motors move the axes (X, Y, Z, and sometimes A, B, C) to position the tool or workpiece precisely along the programmed path.
The spindle rotates at high speeds with tools like drills and milling cutters to perform cutting, drilling, turning, etc. Meanwhile, the workholding table secures the material and moves as needed to achieve the desired shape.
Types of CNC machining machines
CNC machines are divided into three main groups based on function:
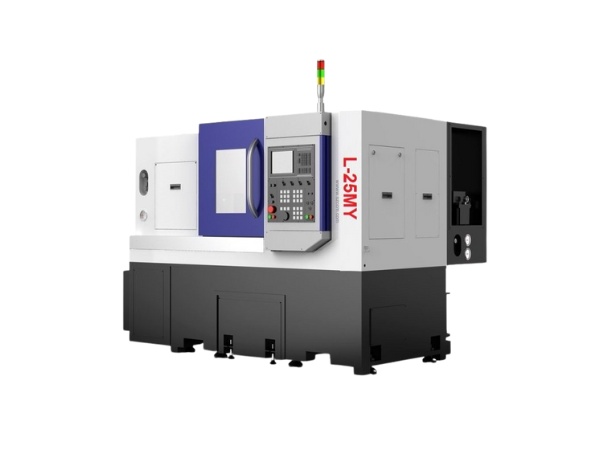
CNC lathes
CNC lathes are primarily used for machining cylindrical parts by removing material while the workpiece rotates. They are widely used in machine shops to improve precision and automate production, reducing labor costs.
Common types include 2-axis lathes (X and Z) and 4-axis lathes with milling capabilities for complex tasks. In Vietnam, CNC lathes are used in both woodworking and industrial component manufacturing.

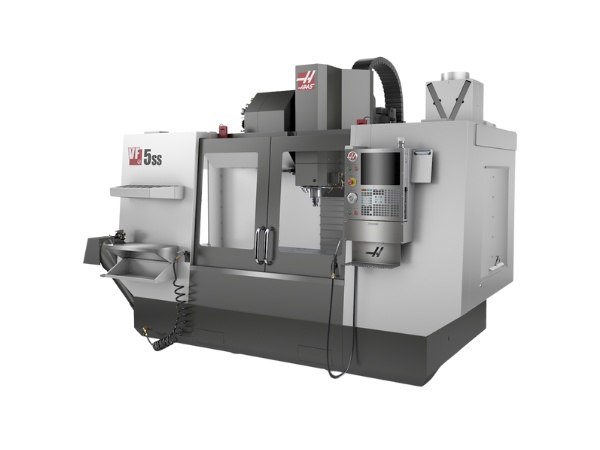
CNC milling machines
CNC mills use rotating cutters to remove material. They can machine flat surfaces, grooves, holes, or complex shapes with high precision and speed. With multiple cutting edges, milling tools last longer and offer better material removal – ideal for mass production.
Though milling can produce vibration, modern CNC machines have addressed this, making milling indispensable in Vietnam’s precision engineering industry.

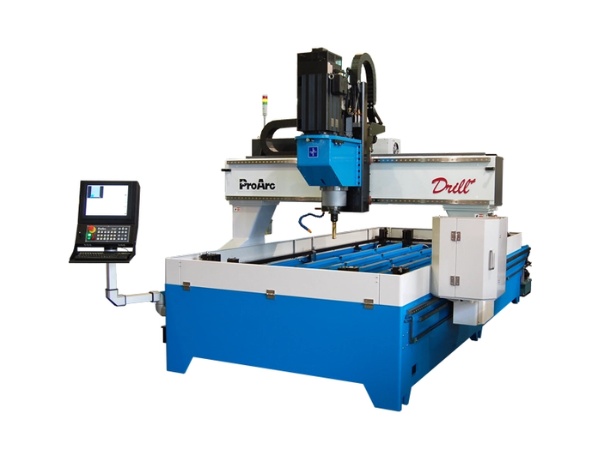
CNC drilling machines
CNC drilling machines specialize in creating holes in various materials, especially useful for large-scale production. Machine choice depends on the part’s shape and size.
Common types include:
- Bench drills: Compact, ideal for wood, light metals, or plastic.
- Radial drills: Larger, floor-mounted machines for heavy-duty drilling of large parts -typically found in industrial workshops.

If you need to machine multiple metal components with high precision, the CNC manufacturing service at 3Dmanufacturer is a reliable choice. Our service leverages Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology to accurately machine metal parts based on CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models provided by customers.
Why choose CNC manufacturing services at 3Dmanufacturer?
- Fast online ordering: Easily configure machining parameters and complete your order in just a few steps.
- Save time and cost: No need to visit the workshop – enjoy a fully remote and convenient production process.
- Wide range of materials supported: Aluminum, steel, and specialty metals.
- High precision and consistent performance: Ideal for projects with strict technical requirements.
- Applicable across industries: Aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and more.
Understanding the structure of CNC machining machines not only helps engineers and managers operate them effectively but also assists in selecting the right machine for specific production needs. When combined with knowledge of their working principles and types – including lathes, mills, and drills – businesses can optimize performance, improve precision, and reduce production costs in modern industry. Should you require further information, feel free to reach out to 3Dmanufacturer for a comprehensive consultation on our CNC machining solutions.