In the era of rapidly advancing digital technology, 3D scanning is gradually becoming an indispensable tool across various modern industries. Thanks to its ability to accurately digitize the shape and dimensions of real-world objects, this technology offers optimal solutions in design, manufacturing, quality control, and even healthcare. Beyond saving time and costs, 3D scanning also opens up numerous opportunities for innovation in how humans interact with the physical world.
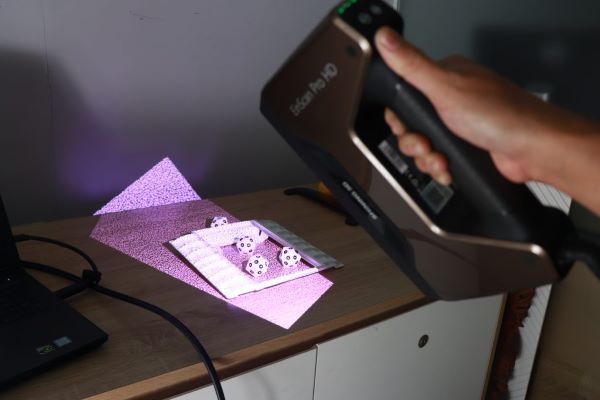

What is 3D scanning?
3D scanning is a technology that captures the shape of physical objects in three-dimensional space and converts them into digital models (CAD). It is considered one of the major advancements of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, making it faster and simpler than ever to create highly accurate replicas of real-world objects.
At its core, 3D scanning is process of collecting geometric data from the surface of an object to build a detailed 3D digital model. This technology has ushered in a new era in design and manufacturing, offering the ability to simulate, edit, and reproduce objects with precision and efficiency.
With its high accuracy and rapid digitization capabilities, 3D scanning is now widely applied in various fields such as mechanical engineering and manufacturing, healthcare, archaeology, transportation, construction, and even in art and heritage preservation. This technology is gradually reshaping the way we design, produce, and interact with the physical world.

How 3D scanners work
Modern 3D scanners primarily use two main light source technologies: laser and structured light. Each technology operates based on different principles and offers distinct advantages, making them suitable for various applications.
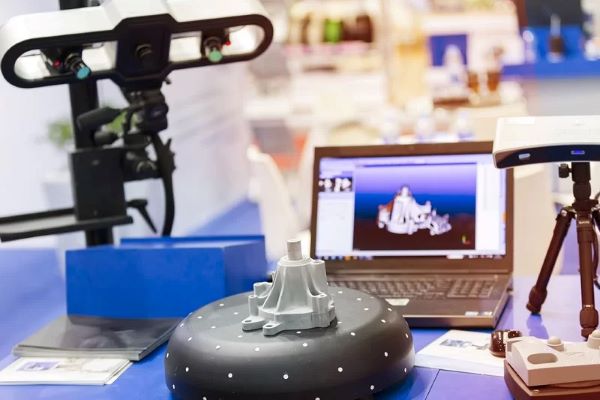

3D scanning with laser technology
Laser scanning technology operates on the principle of projecting one or more laser beams onto the surface of an object. Built-in cameras in the scanner capture the reflected light from the object’s surface. Based on changes in the angle of reflection, the software processes the data to reconstruct the actual shape of the object as a 3D model.
Key Advantages:
- Extremely high accuracy and resolution, especially suitable for applications with strict technical requirements.
- Stable performance in complex lighting environments, with minimal impact from surrounding conditions.
- Capable of scanning dark or shiny surfaces without the need for anti-reflective coating.
Note: Highly glossy, reflective, or transparent surfaces may pose challenges during the scanning process.
3D scanning with structured light
Structured light technology involves projecting a patterned light (usually a series of parallel light stripes) onto the surface of an object. The scanner’s cameras simultaneously capture the deformation of the light pattern as it interacts with different surface geometries. Based on this data, the software reconstructs a highly accurate 3D model of the object.
Key advantages:
- Fast scanning speed, capable of capturing large areas of data within seconds.
- Ensures high accuracy and detailed coverage across the entire surface of the object.
- Eye-safe light source, making it suitable for scanning people and living subjects.
- Widely used in handheld scanners due to its convenience and user-friendliness.
Benefits of 3D scanning technology
Modern 3D scanning technology primarily uses two main light sources: laser and structured light. With near-perfect 1:1 accuracy compared to the original object, 3D scanning offers a wide range of outstanding advantages, especially in design, manufacturing, and quality control. Below are some key highlights:
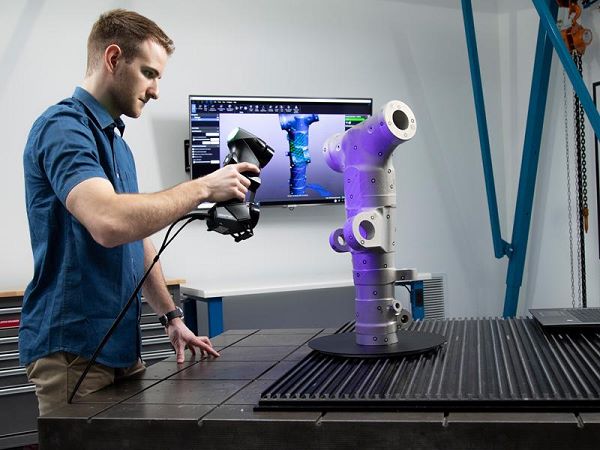

Saving design time
Thanks to its ability to accurately scan three-dimensional shapes using structured light, a 3D scanner can capture every detail and corner of an existing product. This technology supports efficient reverse engineering, significantly reducing the time and effort compared to manual measuring and drafting methods. It also enables faster and more flexible design modifications and adjustments.
Accelerating prototyping
3D scanning allows for precise replication of the shape and dimensions of a physical object, making it easy to generate new designs or replacement parts. The captured 3D data serves as a foundation for assembly, product improvement, and cost optimization in manufacturing, while ensuring greater accuracy than the original sample.
Comprehensive and fast quality control
3D scanning technology not only measures dimensions but also assists in evaluating material properties and object volume. In manufacturing, it helps monitor product quality down to the smallest detail by directly comparing scanned data with CAD models. Visual 3D color maps make it easy to detect deviations, streamlining inspection processes and ensuring product consistency.
Accurate reproduction without original design data
One of the key advantages is the ability to reproduce parts without original CAD design files. Users simply scan the old sample, then use reverse engineering software to generate a new CAD model. The technology also allows for comparison between the new replica and the original scan to accurately detect any deviations.
Comparing designed models with real products
3D scanning enables direct comparison between a design model and the actual manufactured product, ensuring proper fit and precision. It is a powerful tool for quality control and early error detection, helping improve production efficiency and minimize mistakes.
Applications of 3D Scanning Technology in Everyday Life
Although 3D scanning technology has only been introduced to Vietnam in recent years, it has quickly demonstrated its exceptional potential. Today, many large-scale enterprises are boldly investing in and applying this technology to their production processes, gaining impressive benefits in cost savings, time efficiency, and product quality. Below are some key industries effectively utilizing 3D scanning:
Manufacturing & Engineering
In an increasingly competitive market, businesses must constantly innovate and enhance product quality. 3D scanning technology allows companies to scan, analyze, and refine designs directly from physical prototypes, enabling precise product improvements from the initial stages. As a result, the production process becomes more cost-effective, reducing waste from repeated manufacturing iterations. This makes 3D scanning a strategic tool for increasing product value and competitiveness.
Healthcare – Diagnosis and Prosthetics
One of the most remarkable advances of 3D scanning is its application in the medical field. The technology can accurately simulate human body parts, supporting the quick and precise creation of personalized prosthetic limbs, dentures, and other restorative devices. Additionally, 3D models help doctors improve diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical precision compared to traditional methods.
Architecture and Heritage Conservation
3D scanning is becoming an essential tool in architecture, especially for digitizing historical buildings and heritage structures to support restoration and preservation efforts. With just one scanning device, entire structures including trees, interiors, and building facades can be accurately recreated in digital space. In Vietnam, this technology is widely used for heritage data archiving, supporting the preservation of traditional architecture and urban planning.
Machining and Production Control
In precision engineering, 3D scanning is considered a core component of modern manufacturing. Scanners are used not only before production (for analysis and design) but also throughout the fabrication process for real-time quality inspection. After production, the devices are used to compare finished products against original designs to detect discrepancies. Leading companies like VinFast, Hyundai, and Thaco have invested in 3D scanning systems to accelerate timelines, minimize errors, and improve accuracy in mass production.
With its fast, accurate scanning capabilities and versatile applications across numerous sectors, 3D scanning is becoming a key driver of digital transformation and manufacturing modernization. From reverse engineering and quality control to heritage conservation and personalized medicine, this technology enhances operational efficiency and unlocks breakthrough potential for the future. Investing in 3D scanning is a strategic step toward staying ahead in the global technology race. Looking for professional 3D scanning services for your business? Contact 3Dmanufacturer (3Dm) – Vietnam’s leading platform for 3D scanning, 3D printing, and reverse engineering solutions. With a team of experienced technicians and a modern equipment system, 3Dm is ready to accompany you on the journey of digitization and production optimization.